Aug
03

Posted by seancorning on August 3rd, 2021
Posted in: Blog
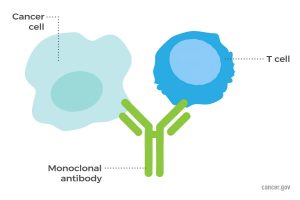
Monoclonal antibodies are biologics often used to treat cancer. (Source: National Cancer Institute)
In recent years there has been a dramatic increase in biologic therapies and immunotherapies approved to help treat a wide variety of diseases and conditions. You may have seen recently in the news that the FDA approved the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin product and wondered what that meant and what biosimilars or biologics are.
Biologics are complex therapies taken from living sources that can then be used as treatments for a variety of illnesses. This can include proteins, blood, vaccines, antibodies, mRNA and many other types of biological molecules.
As the FDA puts it:
“Biological medications (also called biological products) can be made of sugars, proteins, living cells, tissues or a combination of these. They are made from natural and living sources like animal and plant cells, and microorganisms such as bacteria or yeast. Biological medications are usually more complex than other drugs. They are often more complicated to purify, process, and manufacture.”
Due to the complexity of biologics, approved treatments are often biosimilars, which are defined as “a biological product that is highly similar to and has no clinically meaningful differences from an existing FDA-approved” biologic. They aren’t exactly the same as the original biologic but have been proven to have the same effect.
While biologics are becoming more common, they are not new. Insulin is a biologic that has been used since the 1920s as a treatment for type 1 diabetes. More recently, biologic therapies have been used to treat everything from cancer to auto-immune disorders.
Below are some useful resources to learn more about biologics and their applications:
• FDA Fact Sheet on Biologics
• Biologic Outreach Materials
• Biosimilar and Interchangeable Biologics
• Biosimilar Basics
• Cancer Immunotherapy via MedlinePlus